Posted inProfessional Ethics & Human Values
QUESTIONABLE ENGINEERING PRACTICES
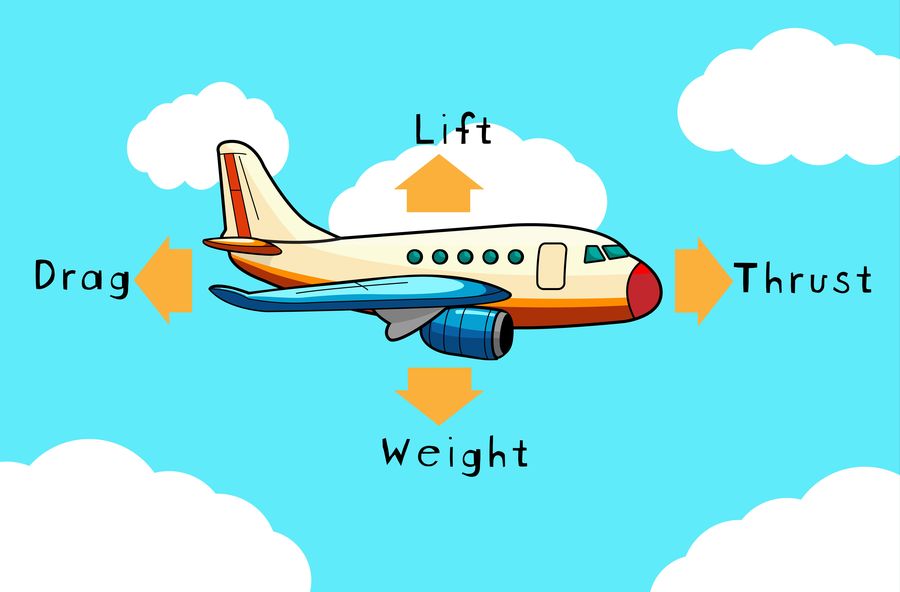
Trimming – “smoothing of irregularities to make data look extremely accurate and precise” Cooking – “retaining only those results that fit the theory and discarding others”. Forging – “inventing some or all of the research data…” Plagiarism – misappropriating intellectual property. Conflicts of interest (such as accepting gifts.) – actual – potential – apparent