Posted inPrinciple of Management
Organizational Change
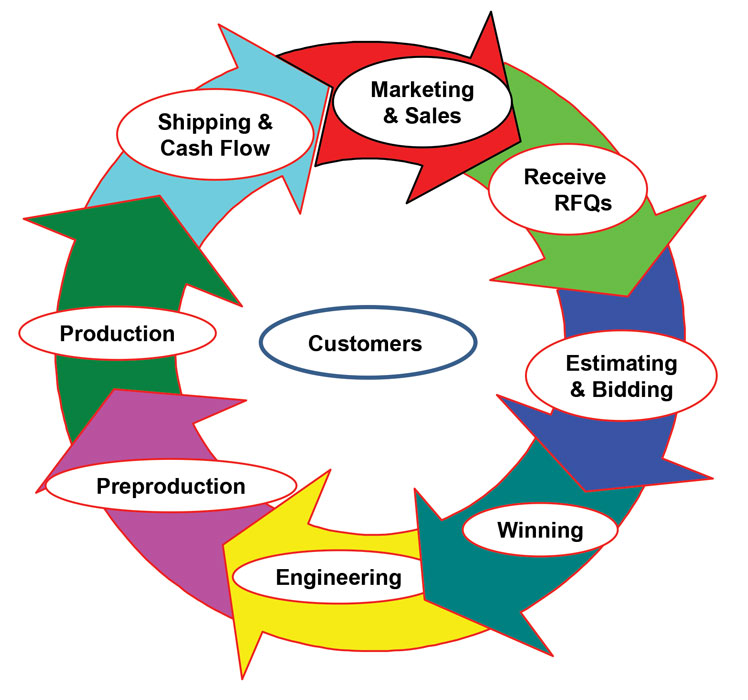
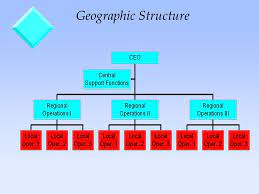
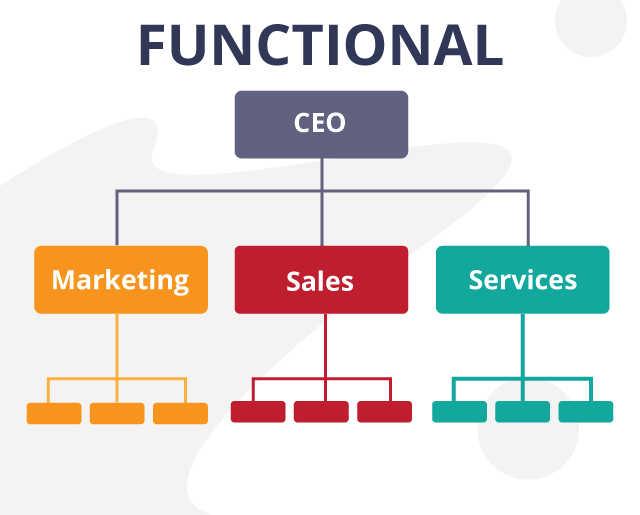
One of the greatest challenges faced by organizations today is the volatility of the global markets. Globalization has greatly affected the market and so have opportunities for more growth and revenue. However, to serve such a diverse marketplace, organizations need to respond to and understand the needs and expectations of the marketplace. Organizations are required to constantly innovate and update their processes and operational efficiencies to collaborate with the expanding markets. Organizations that refuse to change or move forward are forced to exit the market or may be wiped out by forward looking companies. It is this movement or shift in an organization to improve the performance of the entire organization or a part of the organization that is referred to as Organizational Change. Organizational change is a process in which a large company or an organization changes its working methods or aims, in order to develop and respond to new Situations or markets.