Liquid Nitrogen Plant (LNP) extracts Nitrogen gas from the atmospheric air and then liquefies it with the help of Stirling Cryocooler.
Nitrogen can be liquefied by two methods:
a. Distillation of liquid air.
b. Pressure Swing Adsorption system with Cryogenerator
LNP works on the principle of reversed Stirling cycle.
Construction of Liquid Nitrogen Plant
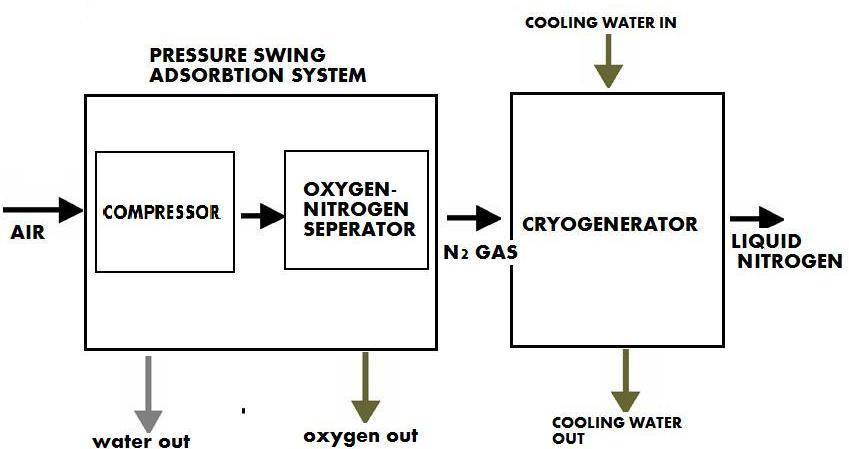
There are mainly two important parts of Liquid Nitrogen Plant.
1. Pressure Swing Adsorption System (PSA)
The main objective of PSA system is to extract Nitrogen gas from compressed atmospheric air.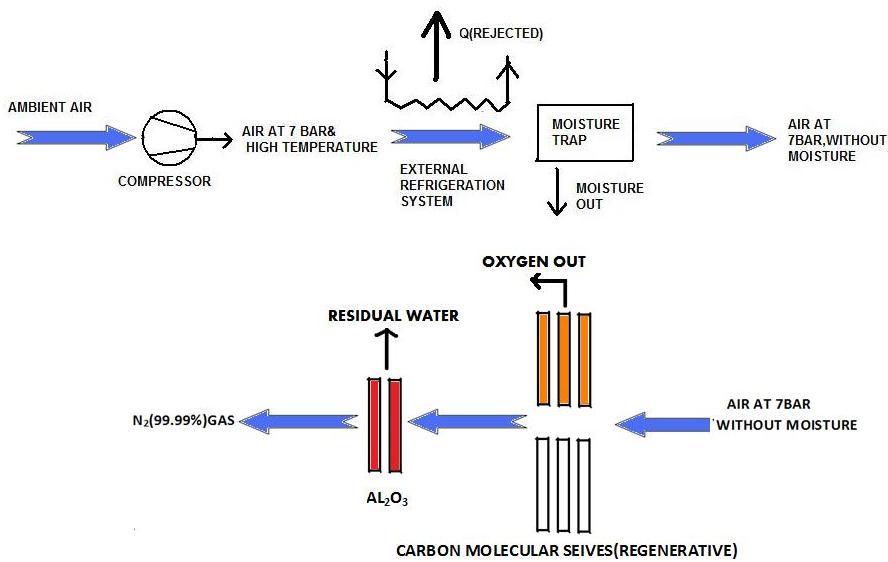
2. Cryogenerator or Cryocooler
It liquefies gaseous Nitrogen to liquid state and liquid Nitrogen is collected in Dewar vessel (vacuum insulated vessel)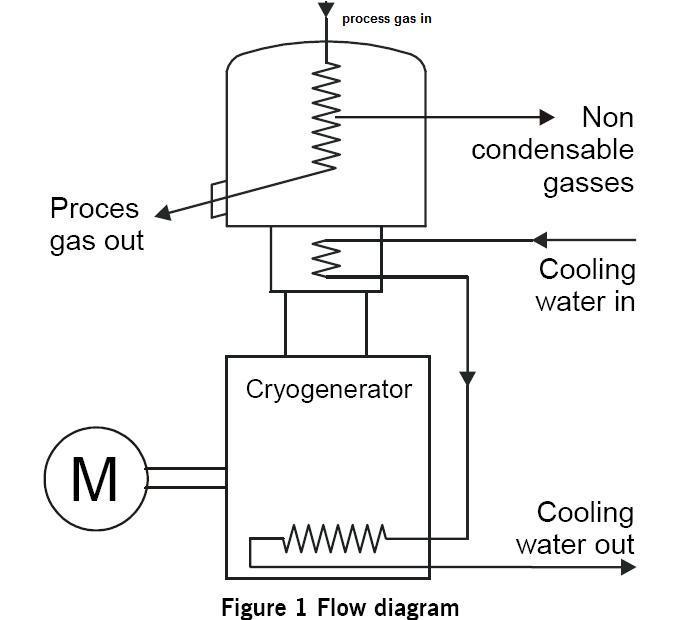
Working principle of liquid Nitrogen plant
- Atmospheric air is sucked into compressor whereby it is compressed to the high temperature about 7 bar pressure with high temperature.
- This high temperature compressed air is cooled in the external refrigeration system.
- Cooled compressed air is then passed through moisture separator to trap the moisture from the air
- This dry compressed air passes through a bed of carbon molecular sieves whereby oxygen and nitrogen from the air are separated and remaining contents of air is purged to the atmosphere.
- Separated Nitrogen is now allowed to pass through Cryogenerator which works on Stirling Cycle which cools the gaseous Nitrogen to a liquid state at 77.2 Kelvin which is the boiling point of nitrogen
- Liquid Nitrogen is now collected in Dewar’s vessel to store it for application purpose
Applications of Liquid Nitrogen
- Serves as coolant for computers and vacuum pump systems
- Cooling of superconductors
- Storage of foods for food preservation
- Cryopreservation of blood
- Cryosurgery for removing dead cells from brain
- Preservation of semen of animals
- Working substance for liquid nitrogen power vehicle and much more.
- Cryo treatment of various metals to improve the properties