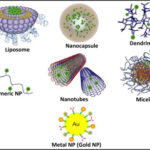
Systems confined in two dimensions, or quasi-1D systems, include nanowires, nano rods, nanofilaments and nanotubes: again these could either be amorphous, single-crystalline or polycrystalline (with nanometre-sized grains). The term ‘nano-ropes’ is often employed to describe bundles of nanowires or nanotubes.
Types of Nanowires:
· Metallic – Made from Nickel, Platinum or Gold
· Semi-conducting – Comprises of Silicon, Indium phosphide or Gallium Nitride
· Insulating – Silicon Dioxide or Titanium dioxide
· Molecular – Involves repeating organic or inorganic molecular units
Synthesis methods:
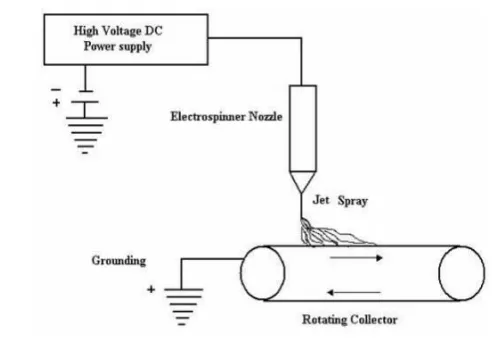
1. Electro-spinning
· Uses an electrical charge to draw very fine (typically on the micro or nanoscale) fibres from a liquid.
· Sufficiently high voltage is applied to a liquid droplet and the body of the liquid becomes charged.
· When the electrostatic repelling force overcomes the surface tension force of the polymer solution, the liquid spills out of the spinneret and forms an extremely fine continuous filament.
· These filaments are collected onto a rotating or stationary collector with an electrode where they accumulate and bond together to form nanofiber fabric.
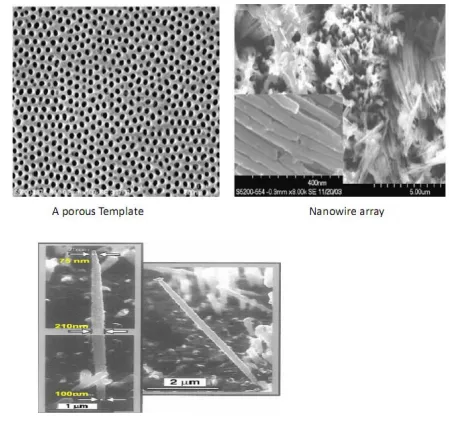
2. Template Base synthesis
· Use in fabrication of nanorods, nanowires, and nanotubes of polymers, metals, semiconductors, and oxides.
· Some porous membrane with Nano-size channels(pores) are used as templates to conduct the growing of nanowires.
· Pore size ranging from 10 nm to 100 mm can be achieved.
Applications of Nanowires:
Nanowires are promising materials for many novel applications for their unique geometry and unique physical properties such as:
· electrical
· magnetic
· optical
· mechanical