Posted inPrinciple of Management
Organizing
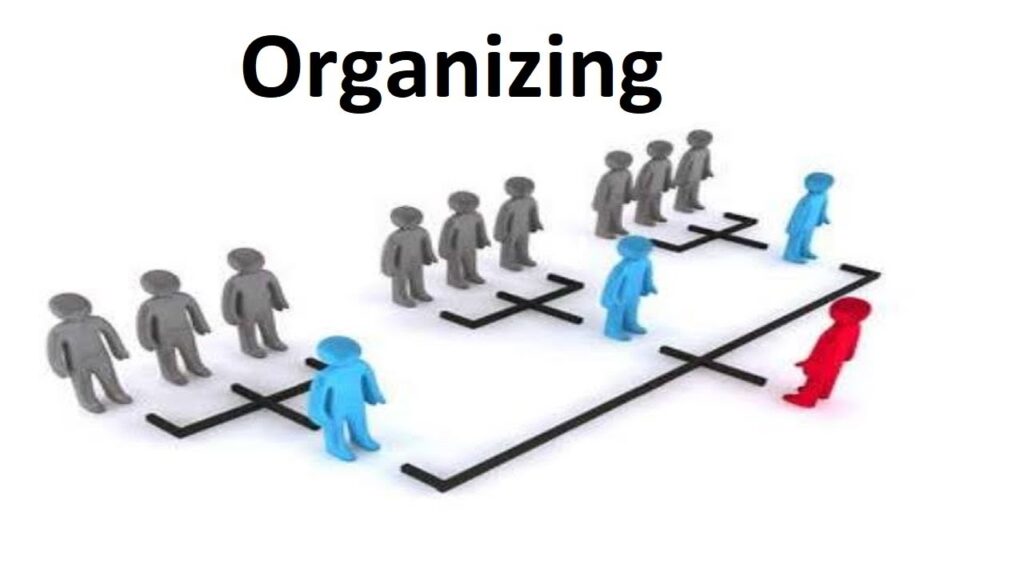
Once a manager has created a work plan, the next phase in management cycle is to organize the people and other resources necessary to carry out the plan. Organizing should also consider the resources and physical facilities available, in order to maximize returns With minimum expenditure. Organizing may be referred to as the process of arranging and distributing the planned Work, authority and resources among an organization’s members, so they can achieve The organization’s goals. Organizing involves the following steps: Creating the organizational structure - The framework of the organization is created within which effort is coordinated allocating human resources to ensure the accomplishment of objectives. This structure is usually represented by an organizational chart, which is a graphic representation of the chain of command within an organization. Making organizational design decisions - Decisions are made about the structure of an organization.…