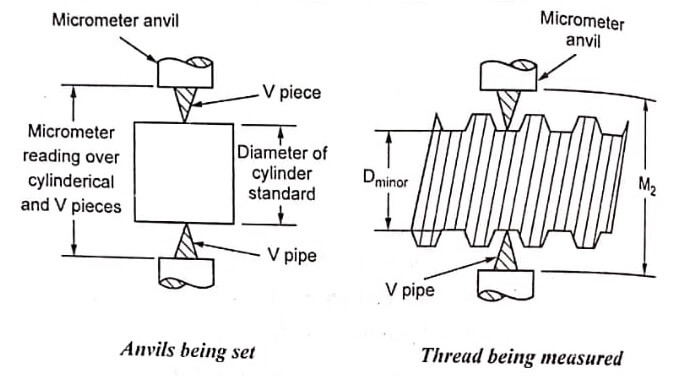
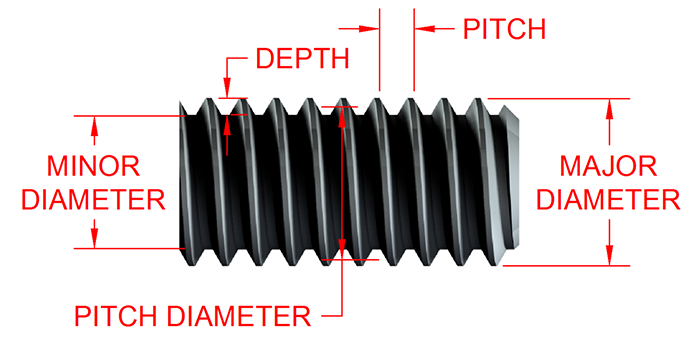
Posted inEngineering Metrology & Measurement
ROUNDNESS MEASUREMENT
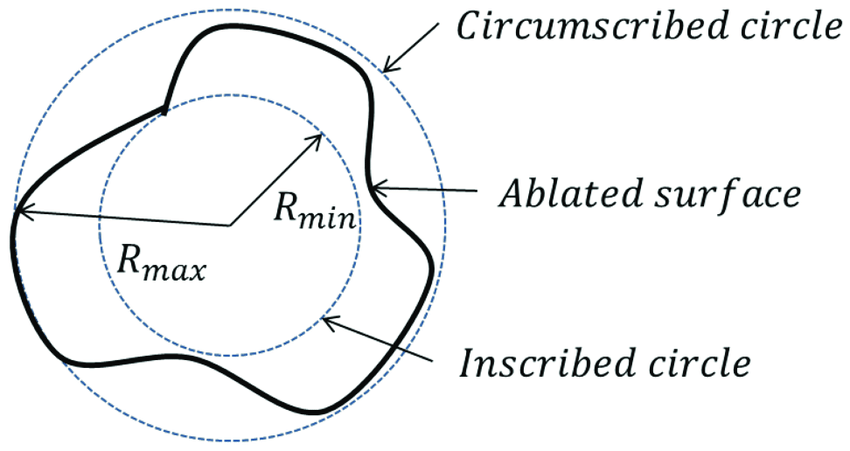
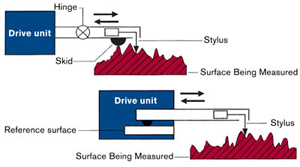
Roundness or circularity: Is the radial uniformity of work surface measured from the centre line of the work piece. Methods of measuring roundness: V- block and dial indicator method Roundness measuring machine