Posted inPrinciple of Management
Delegation
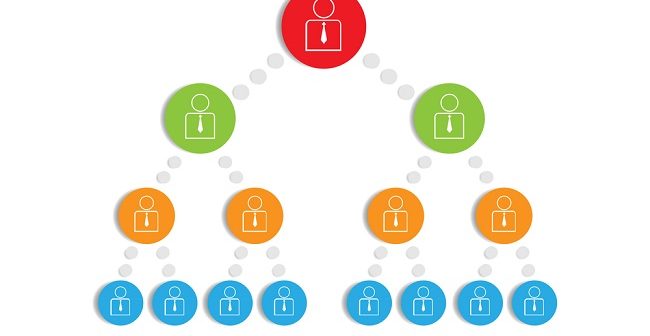
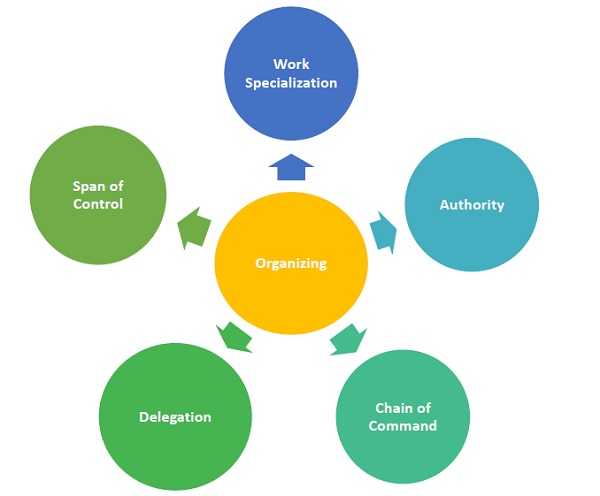
Another important concept closely related to authority is delegation. It is the practice of turning over work-related tasks and/or authority to employees or subordinates. Without delegation, managers do all the work themselves and underutilize their workers. The ability to delegate is crucial to managerial success. Authority is said to be delegated when discretion is vested in a subordinate by a superior. Delegation is the downward transfer of authority from a manager to a subordinate. Superiors or managers cannot delegate authority they do not have, however, high they may be in the organizational hierarchy. Delegation as a process involves establishment of expected outcomes, task assignment, delegation of authority for accomplishing these tasks, and exaction of responsibility for their accomplishment. Delegation leads to empowerment, as employees have the freedom to contribute ideas and do their jobs in the best possible ways.