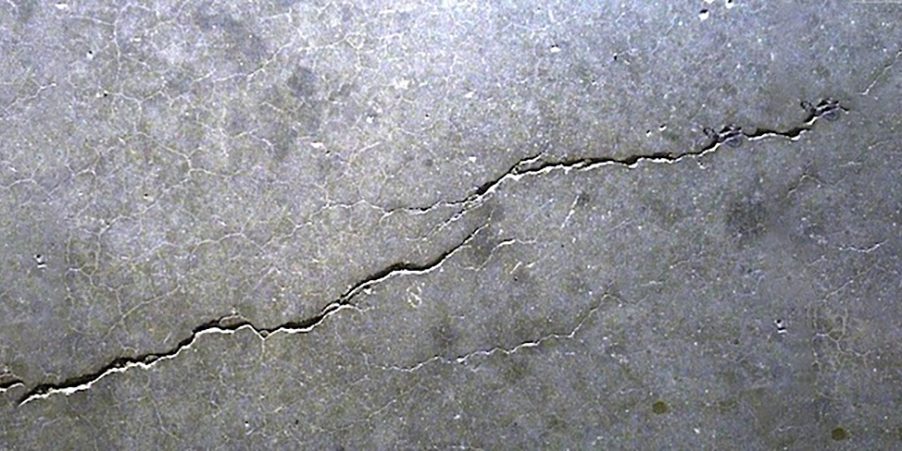
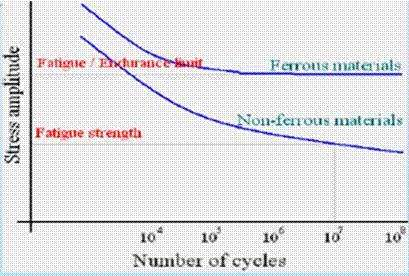
Stages is fatigue failure:
I. crack initiation at high stress points (stress raisers) II. propagation (incremental in each cycle)
III. final failure by fracture
Stage I – propagation
• slow
• along crystallographic planes of high shear stress
• flat and featureless fatigue surface
Stage II – propagation
Crack propagates by repetitive plastic blunting and sharpening of the crack tip.