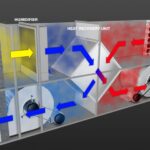
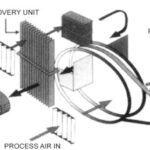
If the condition of the air is changing from state 1 to state 2, consider that the intersection of a horizontal line through state 1 and a vertical line through state 2 occurs at state 0. Then the change in heat can be expressed as:

Where:
• Qs = sensible heat added, Btu
• QL = latent heat added, Btu
• Ma = Mass of dry air, lb [= (volume of air)/(specific volume of moist air in ft3 /lb d.a)]
• h = Enthalpy of air, Btu/lb of dry air
• qs = Rate of sensible heat transfer, Btu/min
• ma = Mass airflow, lb/min [= (volume of moist airflow per min)/(specific volume of moist air in ft3 /lb d.a)]
The rate of moisture addition to the air, Mwater, is determined by a water vapor mass balance:

Where:
• w 2 = humidity ratio of the moist air upstream of the humidifier
• w 0 = humidity ratio of the moist air downstream of the humidifier
Example
Ninety cubic-ft of lumber is dried at 60°C (140°F) dry bulb temperature and 52°C (125.6°F) wet bulb temperature. The drying rate of the lumber is 5.68 lb of water per hour. If outside air is at 27°C (80.6°F) dry bulb temperature and 80% relative humidity, how much outside air is needed per minute to carry away the evaporated moisture?
Solution
a) Locate the 80.6°F dry bulb and 80% Relative humidity as Node 1.
b) Locate the 140°F dry bulb and 125.6 °F wet bulb temperature as Node 2.
c) Move from point established in a) above to right to 100°F on a horizontal dry bulb temperature scale – this corresponds to 39.6% Relative humidity.
The condition of the air is changing from state 1 to state 2
d) Read absolute humidity w2 and w1
• w2 = 0.092 lb/lb dry air
• w1= 0.0185 lb/lb dry air
e) Estimate moisture gain : ∆HR = [w2 – w1] lb/lb dry air
• ∆HR = (0.092 – 0.0185) lb/lb dry air
• ∆HR = 0.0735 lb/lb dry air
f) Estimate drying air:
w = drying rate/∆HR
• w = (5.68 lb/hour)/ (0.0735 lb/lb dry air) = 77.28 lb dry air/hour
g) Estimate volumetric air flow rate for drying:
V = w x specific volume
• V = (77.28 lb dry air/hour) x (13.95 ft3 /lb dry air) = 1078 ft3 /hour