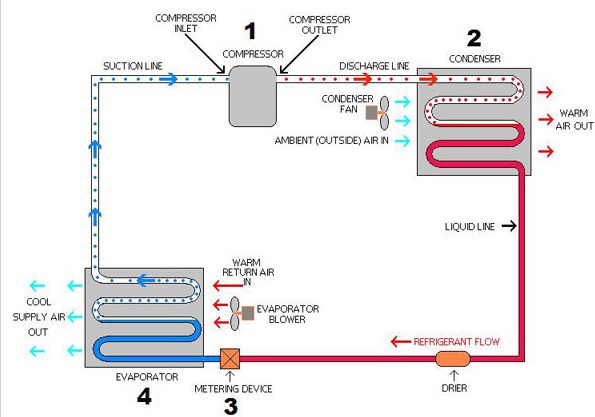
Evaporator is a heat exchanger which removes the heat from stuffs or foods to be cooled by evaporating (Evaporation condition: BP < Evaporation temperature) the low pressure liquid refrigerant while passing through it. At low pressure, Boiling Point (BP) of refrigerant is low, well below room temperature, thus when exposed to room temperature, liquid refrigerant starts evaporating by taking heat from foods, thus foods get cooled). Once the complete evaporation of refrigerant takes place,It has now no more capacity to absorb the heat from foods. And again it needs low pressure liquid form to gets evaporated.
Refrigerant can only gets condensed (liquid form) in condenser (at room temperature condition). But at room temperature condition, refrigerant is well above its BP, so it cannot be converted to lower phase i.e. liquid phase and will remain in vapour form (Room temperature > BP of refrigerant).
Hence, it needs higher BP than room temperature so that condensation can take place at room temperature. BP is a function of pressure, higher the pressure of refrigerant, higher the BP and vice versa. Thus, Compressor is used to raise the pressure of low pressure vapour refrigerant. At the outlet of compressor, vapour refrigerant is in high pressure and high temperature condition. Due to high pressure, BP of refrigerant is now well above the room temperature and it can now easily condensed in condenser by rejecting heat to room temperature air (Condensation condition: BP > Condensation temperature). The amount of heat is now summation of heat taken at evaporator plus heat of compression at compressor.
Thus, at outlet of condenser, refrigerant is at high pressure and is in liquid form. But again, to get lower boiling point well below the room temperature, this high pressure should be again reduced to low pressure condition of evaporator. To reduce the pressure, high pressure liquid refrigerant is now passed through the capillary tube which has high length and lower inside diameter. Thus while passing throught the capillary tube, due to friction, pressure is reduced and partial cooling takes place as boiling point reduction starts (along with evaporation).
Now, low pressure liquid refrigerant (having BP is well below the room temperature) enters the evaporator and start evaporating at room temperature by taking heat of foods to reduce its temperature. And CYCLE continues.
Let us analyse the situation.
Q1 = Heat absorb at evaporator
Q2 = Heat rejected at condenser
W = Work of compressor
The relation is now, Q2 = Q1+W
Thus, Q2 > Q1
In closed door situation, Q2 > Q1 (as Q1 will be absorbed from evaporator compartment only)
Thus, in closed door situation, there is no change in the room temperature as usual.
In OPEN door situation, Q1 will be addition of heat taken from foods and entire room, which eventually increase the Q2. So, there will be increase in temperature of room if door is kept open.