As an engineer, I often use the fact that formulas share a single common factor in order to set them equal to each other, which enables me to solve for a variable contained within one of them. Using this approach we’ll calculate the velocity, or speed, at which the broken bit of ceramic from the coffee mug we’ve been following slides across the floor until it’s finally brought to a stop by friction between it and the floor. We’ll do so by combining two equations which each solve for kinetic energy in their own way.
Last time we used this formula to calculate the kinetic energy, KE, contained within the piece,
KE = FF × d (1)
and we found that it stopped its movement across the floor when it had traveled a distance, d, of 2 meters.
We also solved for the frictional force, FF, which hampered its free travel, and found that quantity to be 0.35 kilogram-meters/second2. Thus the kinetic energy contained within that piece was calculated to be 0.70 kilogram-meters2/second2.
Now we’ll put a second equation into play. It, too, provides a way to solve for kinetic energy, but using different variables. It’s the version of the formula that contains the variable we seek to calculate, v, for velocity. If you’ll recall from a previous Topic, that equation is,
KE = ½ × m × v2 (2)
Of the variables present in this formula, we know the mass, m, of the piece is equal to 0.09 kilograms. Knowing this quantity and the value derived for KE from formula (1), we’ll substitute known values into formula (2) and solve for v, the velocity, or traveling speed, of the piece at the beginning of its slide.
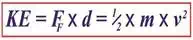
Combining Kinetic Energy Formulas to Calculate Velocity
The ceramic piece’s velocity is thus calculated to be,
KE = ½ × m × v2
0.70 kilogram-meters2/second2= ½ × (0.09 kilograms) × v2
now we’ll use algebra to rearrange things and isolate v to solve for it,
v2 = 2 × (0.70 kilogram-meters2/second2) ÷ (0.09 kilograms)
v = 3.94 meters/second =12.92 feet/second = 8.81 miles per hour.


