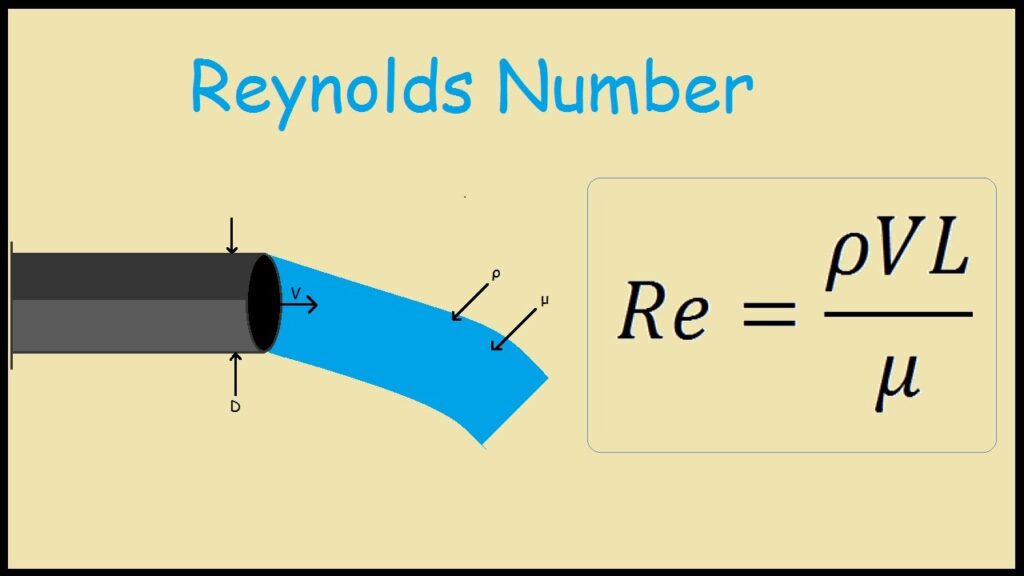
Reynolds number (Re) is an experimental number used to predict the flow velocity in fluid flow at which turbulence will occur. It is a non-dimensional velocity can be defined as the ratio of a fluid’s inertia force to the viscous forces.

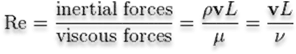
Where,
ρ = mass density of the fluid,
v = Velocity of the fluid,
L = The characteristic linear dimension, (travelled length of the fluid; hydraulic diameter when dealing with river systems),
μ = Dynamic viscosity of the fluid,
v = Kinematic viscosity of the fluid.
Reynolds number is used to determine whether a flow of a fluid will be laminar, turbulent or transitional flow. Below a critical Reynolds number, flow will be laminar. Above a critical Reynolds number, flow will be turbulent.