The Rise of Smart Factories: How IoT and Mechanical Engineering Combine
In recent years, the industrial landscape has undergone a seismic shift, with the advent of smart factories leading the way towards a more efficient, interconnected future. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) with mechanical engineering is revolutionizing the manufacturing process, bringing with it a plethora of benefits that include increased productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced operational efficiency. But what exactly does this mean for the factories of tomorrow, and how is this fusion shaping the future of manufacturing?
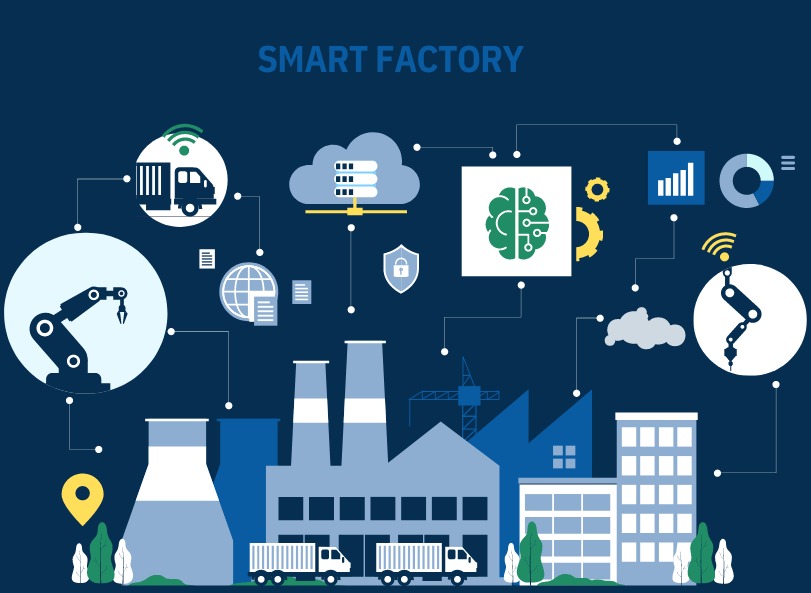
The Concept of Smart Factories
Smart factories are often characterized by their use of advanced technologies, such as IoT devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics, to create a highly flexible, automated, and data-driven production environment. These factories utilize interconnected machinery and systems that communicate seamlessly, enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making processes. This shift from traditional manufacturing to smart factories not only optimizes production but also enhances worker safety and product quality.
The Role of IoT in Smart Factories
At the heart of smart factories lies the Internet of Things. IoT refers to the network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that allow them to connect and exchange data. In a smart factory setting, IoT devices can monitor equipment performance, track inventory levels, and even predict maintenance needs before equipment failure occurs.
For instance, sensors placed on machinery can relay information about temperature, vibration, and operating speed, alerting operators to any anomalies that may indicate a malfunction. This predictive maintenance capability reduces unplanned downtime, saving companies significant amounts of money and time. Moreover, IoT enables manufacturers to create more agile supply chains, allowing for quick adjustments in response to market demands.
The Integration of Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering plays a vital role in the development and implementation of smart factory technologies. Engineers are tasked with designing and optimizing machinery that can effectively utilize IoT data. This includes creating machines that are not only efficient but also capable of self-diagnosis and adaptation based on real-time data inputs.
Moreover, mechanical engineers are involved in the integration of robotics into smart factories. Automated systems, such as collaborative robots (cobots), work alongside human operators to streamline processes and enhance productivity. The combination of mechanical engineering principles with IoT capabilities results in machines that are smarter, more reliable, and better suited to the demands of modern manufacturing.
Conclusion
The convergence of IoT and mechanical engineering is paving the way for a new era in manufacturing. Smart factories represent the future of industrial production, making processes more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. As technology continues to evolve, we can only expect to see further advancements that will shape the manufacturing landscape, creating opportunities for innovation and growth in the industry. Embracing this transformation is no longer an option but a necessity for manufacturers looking to thrive in a competitive global market.