The objective of Electronic Fuel Injection System is to regulate and optimize the fuel/air ratio that enters a vehicle’s engine. Fuel injection has recently become the main fuel delivery system used in automotive petrol engines. It optimizes the fuel/air ratio entering a vehicles engine. EFI System has almost completely replaced usage of carburetors.
Carburetors are good for performance, but due to their vague nature, they can’t make great horsepower, get solid gas mileage, and pass an emission test, all with the same tune, they also had many mechanical parts that could become gummy over period. This means they were more maintenance-intensive, with a carburetor rebuild often being part of a routine maintenance schedule.
The initial EFI was mostly just processor controlled carburetors attached to an oxygen sensor and throttle position sensor, all wired to an Electronic Control Unit. The Electronic Fuel Injection System consists of electronic components and sensors. It has to be kept clean and well calibrated to boost the engine’s strength and efficiency and to cut down gas consumption.
Parts Of An Electronic Fuel Injection System
Components of the Electronic Fuel Injection System include:
- Sensors
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
- “Check Engine” Light / “Service Engine Soon” Light
- Fuel Injectors
- Fuel Pump
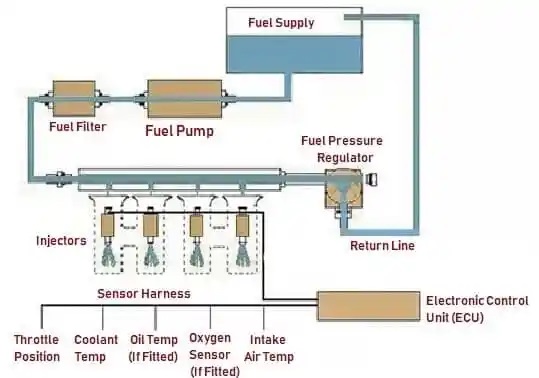
Sensors
Sensors are installed in numerous points of the engine and their function is to send out information to the ECU. The following sensors are used:
- Engine Temperature Sensor
- Intake Temperature Sensor
- Exhaust Temperature Sensor
- Engine Speed Sensor
- Throttle Position Sensor
- Probe which is responsible for the measurement of the fuel concentration in the fuel/air mixture
Actuators are components that obtain information from ECU and they act in the feeding system, varying the volume of fuel that the engine receives.
It uses following actuators:
- Fuel Injector
- Spark Plug
- Throttle
Electronic Control Unit
The Electronic Control Unit is responsible for the measurement of the sensors and the estimation of the action for each actuator with regard to timing restrictions. The time constraints of the system are imposed by the characteristics of the internal combustion engine to be controlled.
It is defined that a turn of the engine i.e. 360° is completed once in every 5 micro seconds for 12,000 rpm. The actuator of throttle valve considers the position of 0° as a pulse of 1 milli second and 90° as a pulse of 2 milli seconds, within a period of 25 milli seconds. Considering these timing constraint, the reading of the sensors and the calculation of the acting times for the actuators should be processed in at most 15 milli seconds.
“Check Engine” Light / “Service Engine Soon” Light
The “Check Engine” Light (or “Service Engine Soon” Light) on the console comes on during the scan and goes off when all sensors are functional.
Fuel Injector
It helps in injecting fuel into the engine’s intake ports.
Fuel Pump
It helps in pumping gasoline from the vehicle’s fuel tank to the engine and distributes fuel to Fuel Injection System under higher pressure.
How EFI System Works
The Fuel Injection System consists of many sensors positioned all around your vehicle. Every time you start your vehicle, the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) scans each and every one of these sensors to verify their functionality.
The “Check Engine” Light (or “Service Engine Soon” Light) on the console comes on during the scan and goes off when all sensors are functional.
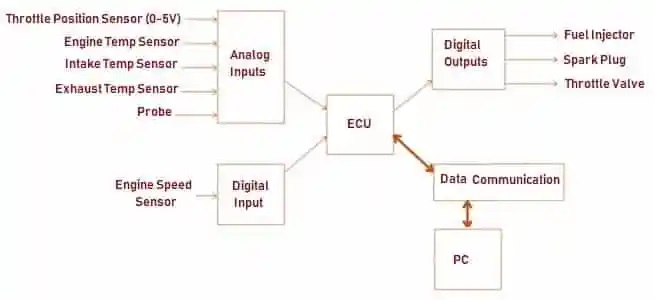
The sensors continuously detect the values of numerous parameters like air pressure, air temperature, throttle angle, air density, fuel temperature, fuel pressure, oil pressure, coolant temperature, exhaust temperature, crankshaft angle, timing, engine rpm, speed, etc.
All these data are processed through the ECU (Electronic Control Unit) to establish the amount of time the Fuel Injectors are open, injecting fuel into your engine’s intake ports. The injectors usually are open only for a few milliseconds at a time. A fuel injector consists of a nozzle and a valve. The power to inject the fuel comes from a Fuel Pump or Pressure Container located far back in the fuel supply. The fuel going through the system is atomized by forcibly pumping it through a small nozzle under very high pressure.
Advantages of Electronic Fuel Injection System
The advantages are:
- Enhancement of volumetric efficiency of the engine.
- Direct fuel injection into the cylinder eliminates manifold wetting.
- Good atomization of fuel even at low speed as atomization is independent of cranking speed.
- Less knocking because of the improved atomization and vaporization.
- Ice formation at throttle plate is eliminated.
- Fuels of low volatility can be used as distribution is independent of vaporization.
- As variation of fuel/air ratio is almost negligible it results in good engine performance.
- The height of engine can be less as the position of injection unit is not so critical.
Disadvantages of Electronic Fuel Injection System
The disadvantages include:
- High maintenance cost.
- Difficulty in servicing.
- Possibility of malfunction of some sensors.


