A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel.
The National Emissions Standards Act, an amendment made in 1965 to the Clean Air Act, set the first federal vehicle emissions standards. Each state has regulations that adhere to federal standards, with many states requiring that all registered cars be tested to evaluate the output of emissions.
The modern exhaust system on vehicles features a range of parts that helps control emissions and make them more environmentally friendly. Among these parts is a catalytic converter, which helped many car manufacturers meet the standards set by the National Emissions Standards Act.
A catalytic converter is an important part of the exhaust system.
What Does a Catalytic Converter Do?
A catalytic converter uses a chamber called a catalyst to change the harmful compounds from an engine’s emissions into safe gases, like steam. It works to split up the unsafe molecules in the gases that a car produces before they get released into the air.
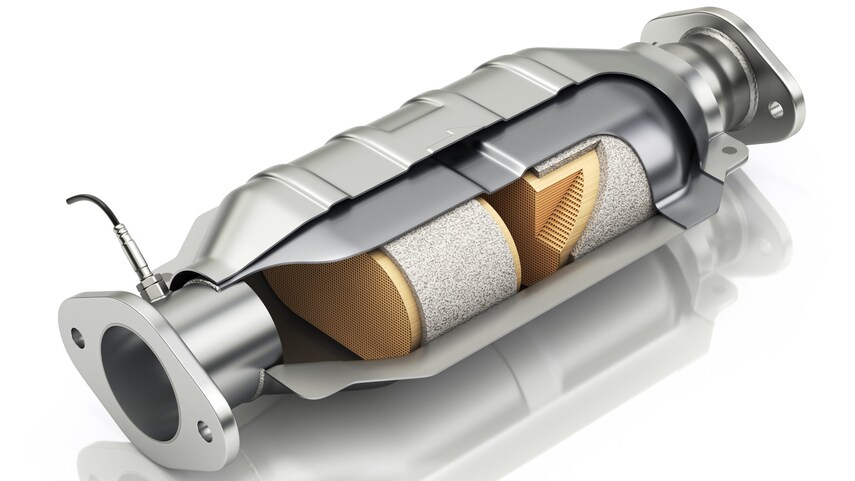
The catalytic converter is located on the underside of a vehicle and looks like a large metal box. There are two pipes coming out of it. The convertor utilizes these two pipes and the catalyst during the process of making the gases safe to be expelled.
Gases are brought in from the “input” pipe connected to the engine of a vehicle. These are blown over the catalyst, which causes a chemical reaction that breaks apart the pollutants. The less-harmful gases now travel through the second pipe, or the “output,” that is connected to a car’s tailpipe.

What Is Inside a Catalytic Converter?
So what is a catalytic converter made of? The catalyst inside a catalytic converter is made typically from platinum or a similar metal, such as rhodium or palladium. Gases flow through a ceramic honeycomb structure located within the cat housing. This is lined with metals that have specific jobs that play a role in reducing emissions. There are two main types of catalysts that might be featured in a car:
- Reduction catalysts: Help reduce nitrogen oxide pollution by removing oxygen. Nitrogen oxides are broken up into nitrogen and oxygen gases, which on their own are harmless.
- Oxidation catalysts: Used to change carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide through an opposite process of adding oxygen.
Also located near the catalytic converter is an oxygen (O2) sensor, which works to tell a car’s electronic control unit (ECU) how much oxygen is found in the exhaust gases. This helps a vehicle run on a more efficient air/fuel ratio, allowing the engine to supply the converter with enough oxygen to complete the oxidation process.
Types of Catalytic Converters
As mentioned before, there are two primary catalysts – reduction and oxidation – that can be used within an exhaust system to handle specific gases.
Depending on the year of the vehicle and the type of catalytic converter it has, there might not be a reduction catalyst in place. There are two primary kinds of catalytic converters:
- Two-way: The two-way catalytic converter was present on vehicles in the United States until 1981. They only have oxidation catalysts, which help change carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. Hydrocarbons (which is unburned and partially burned fuel) are changed to carbon dioxide and water.
- Three-way: Since 1981, the three-way catalytic converter has been used. This performs the same as the two-way converter with the addition of a reduction catalyst. As stated earlier, this is used to change nitrogen oxides to nitrogen and oxygen gases.
Diesel engines employ the use of two-way catalysts, and the converters are also specifically designed to work with diesel exhausts. The converters for these types of engines try and target particulates known as soluble organic fractions. These are made from hydrocarbons bound to soot.

