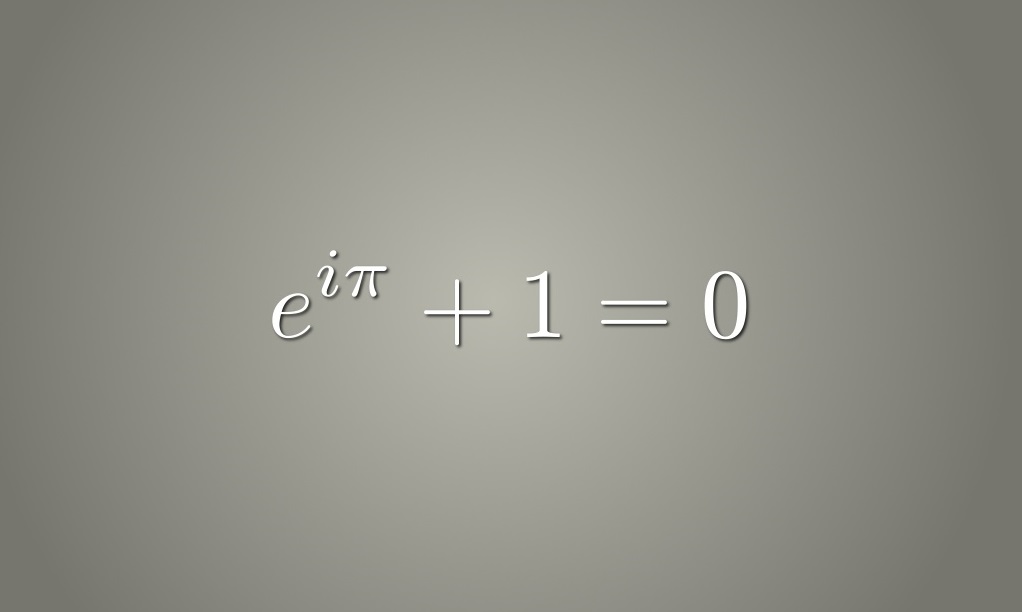The Euler’s equation in the differential form for the motion of liquids is given as follows:
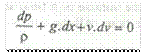
This equation is based on the following assumptions:
(a) The fluid is non – viscous.
(b) The fluid is homogeneous and in-compressible.
(c) The flow is continuous, steady and along the streamline.
(d) The velocity of flow is uniform over the section.
Note: The Bernoulli’s equation is obtained by integrating the above Euler’s equation.