and minimum
and minimum normal stresses
normal stresses
ii. Can be found out by taking derivative of  with respect the angle
with respect the angle  and we will get
and we will get

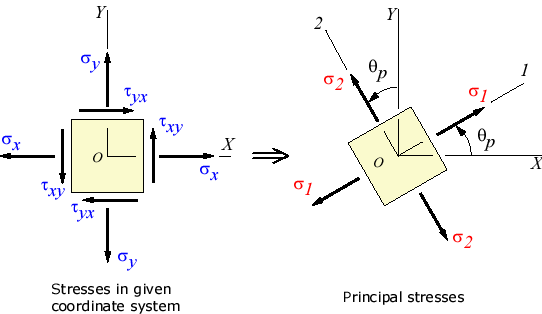
1. This  has two values differ by 90o they are known as principal angles.
has two values differ by 90o they are known as principal angles.
2. They also represent orientation of planes known as principal planes.
3. One value of angle represents maximum stress and other minimum stress.
4. From 1st point we can say that principal stresses occur on mutually perpendicular axes
iii. Substituting the values of  in the original equation we will get the value of maximum and minimum normal stress i.e.
in the original equation we will get the value of maximum and minimum normal stress i.e.  respectively
respectively

 is maximum or minimum
is maximum or minimum  = 0
= 0
F The principal planes for elements in uniaxial stress and biaxial stress are the x and y planes themselves.
F For an element in pure shear, the principal planes are oriented at 45° to the x axis
b. Maximum Shear stress
i. Like principal stress we can find out maximum shear stress also. By taking derivative of with respect the angle
with respect the angle  and we will get
and we will get

1. This  has two values differ by 90o
has two values differ by 90o
2. The maximum and minimum values only differ by sign the magnitude is same
3. Comparing the formulae of  and
and  we get
we get


The above equation shows that the planes of maximum shear stress occur at 45° to the principal planes
ii. Substituting the values of  in the original equation we will get the value of maximum
in the original equation we will get the value of maximum

iii. There is one alternate expression for 

F Normal stresses have same value when  is maximum or minimum i.e.
is maximum or minimum i.e. 
F In the particular cases of uniaxial stress and biaxial stress the planes of maximum shear stress occur at 45° to the x and y axes.
F In the case of pure shear the maximum shear stresses occur on the x and y planes