Amagat’s Law
The volume of an ideal gas mixture (V) is equal to the sum of the component volumes (Vj’s) of each individual component in the gas mixture at the same temperature (T) and total pressure (P) of the mixture. For example

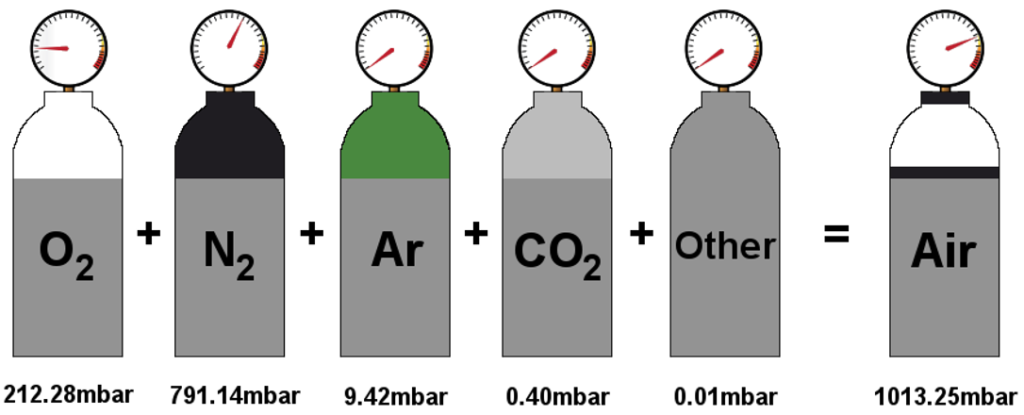
Dalton’s Law
The total pressure (P) of an ideal gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures (pj’s) of each individual component in the gas mixture at the same temperature (T) and total volume (V) of the mixture. For example,