Air conditioning is the process of maintaining comfortable conditions inside a closed space. It controls temperature, humidity, air flow rate and the cleanliness of air inside a room.
Sitting in a cool room, have you ever wondered how come you are feeling comfortable while the temperature in the surrounding areas is very high? Scientists have found that humans feel most comfortable at temperatures around 25 degree Celsius and humidity of 50% with certain flow rates of air. This is called a comfort zone. At this temperature and humidity, humans are able to work at their maximum efficiency. Air conditioning is the process of maintaining specific temperature, relative humidity, specific flow rate of air and low dust levels inside an enclosed space.
Every human being gives up about 100Kcal of heat per hour. Heat is also given up in the room by other sources like lights, coffeemaker, etc. The walls and the roof of a room absorb heat from the surroundings. A lot of sun heat comes into rooms from windows. All this heat increases the temperature inside the room and makes us uncomfortable. The function of the air conditioning system is to absorb this heat and throw it to the surroundings thereby maintaining low temperature inside the room. It also absorbs the excess amount of dew inside the room and maintains humidity levels inside the room. The fan inside the air conditioner maintains proper flow of air inside the room, while the filter cleans and purifies the air.
Air conditioning serves a dual purpose. If the surrounding temperature is higher than the comfort temperature of 25 degree Celsius, it acts as a cooler whereby it keeps the room cool. On the other hand, if the surrounding temperature is too low, it acts as a heater and increases the temperature inside the room. There is a valve in the air conditioner which enables us to change its functioning. But more commonly, air conditioning is used to maintain temperatures lower than the surroundings and specific levels of humidity.
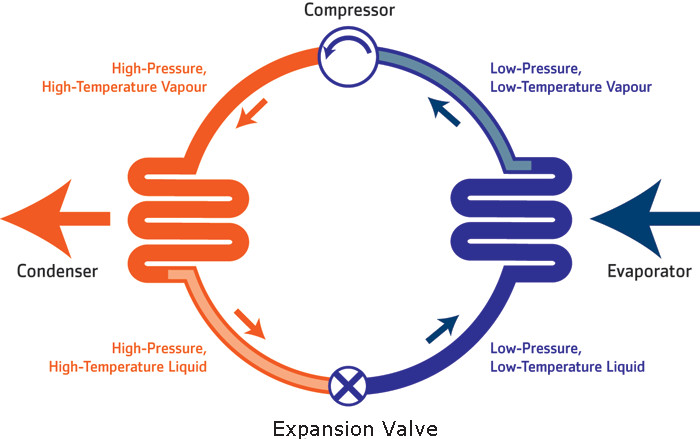
Some of the important parts of air conditioning systems are: compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator. To transfer the heat from a room to its surroundings, some media is required. The media used in air-conditioning systems is a fluid called Freon.
Air conditioning systems come in various capacities with different flow rates of air. The capacity of an air conditioner is measured in terms of tonnage. If the capacity of an air conditioner is one ton, it can remove 3024Kcal of heat from a room in an hour. If the size of a closed space is large and the number of people is also large, the amount of heat generated inside the room is very high; hence more heat is to be removed and larger capacity air conditioners are required. For smaller rooms, air conditioners of about 1 ton are good enough to maintain comfort conditions.