I.C. Engines: Internal combustion engine more popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel inside the engine cylinder, into mechanical work. Its versatile advantages such as high efficiency light weight, compactness, easy starting, adaptability, comparatively lower cost has made its use as a prime mover universal
Classification of I.C. Engines: I.C engines are classified according to:
1. Nature of thermodynamic cycles as:
1. Otto cycle engine
2. Diesel cycle engine
3. Dual combustion cycle engine
2. Type of the fuel used:
1. Petrol engine
2. Diesel engine
3. Gas engine
4. Bi-fuel engine
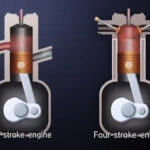
3. Number of strokes as
1. Four stroke engine
2. Two stroke engine
4. Method of ignition as:
1. Spark ignition engine, known as SI engine
2. Compression ignition engine, known as C.I. engine
5. Number of cylinder as:
1. Single cylinder engine
2. Multi cylinder engine
6. Position of the cylinder as:
1. Horizontal engine
2. Vertical engine
3. Vee engine
4. In-line engine
5. Opposed cylinder engine
7. Method of cooling as:
1. Air cooled engine
2. Water cooled engine