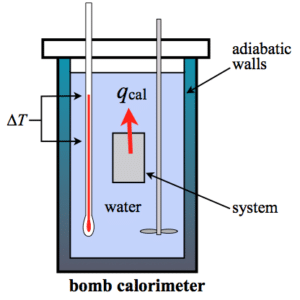
Mainly two types of calorific values are there – Higher Calorific Value and Lower Calorific Value .
Higher Calorific Value (HCV) or Higher Heating Value (HHV) or Gross Calorific Value: When 1 kg of a fuel is burnt, the heat obtained by the complete combustion after the products of the combustion are cooled down to room temperature (usually 15 degree Celsius) is called higher calorific value of that fuel.

Lower Heating Value (LLV) or Lower Calorific Value (LCV) or Net Calorific Value: When 1 kg of a fuel is completely burned and the products of combustions are not cooled down or the heat carried away the products of combustion is not recovered and the steam produced in this process is not condensedthen the heat obtained is known as the Lower Calorific Value.
Relation between Higher and Lower Calorific Value.
Answer: The amount of Lower Calorific Value can be obtained by subtracting the amount heat carried away by the combustion products especially the heat carried away by the steam
LCV = HCV – Heat carried away by the steam.