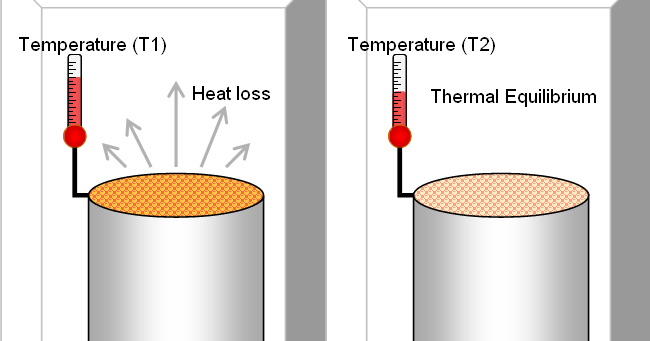
A thermodynamic system is said to exist in state of thermodynamic equilibrium when no change in any macroscopic property is registered, if the system is isolated from its surroundings.
An isolated system always reaches in course of time a state of thermodynamic equilibrium and can never depart from its spontaneously.
Therefore, there can be no spontaneous change in any macroscopic property if the system exists in an equilibrium state.
A thermodynamic system will be in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium, if the system is the state of Mechanical equilibrium, Chemical equilibrium and Thermal equilibrium.
1. Mechanical equilibrium: The criteria for Mechanical equilibrium is the equality of pressures.
2. Chemical equilibrium: The criteria for Chemical equilibrium is the equality of chemical potentials.
3. Thermal equilibrium: The criteria for Thermal equilibrium is the equality of temperatures.